Feb
Microsoft Server Customization
Windows Server® 2000 2003 2008 2010 2012 and 2016 includes Server Manager, a new tool with which administrators can either install or remove server roles, or manage those roles after they are installed. Server Manager provides centralized control of a server, regardless of the combination of roles installed.
You can customize the Commerce Server unified operation sequence by altering the execution of the operation sequence components. You can remove operation sequence components or create new ones, therefore providing the ability to configure the requirements of each business operation. Developers can extend the operation response or create new operations responses.
Developers can extend a commerce entity by adding new properties or relationships to existing commerce entities.
Server Manager alleviates the need for administrators to use multiple tools in order to install, secure, and manage a server role. Server Manager installs server roles that are secure by default. With Windows Server 2008 R2 installed, there is no longer a need to run the Security Configuration Wizard (SCW) following a server role installation to configure services and ports for the role.
In this Section
2.Adding Features to Your Server
4.Configuring the Windows Firewall
5.Adding Roles to Your Server
In Windows Server 2008 or higher version of server they also identify R2, you can add roles to the server by using the Add Roles Wizard, Windows PowerShell cmdlets for Server Manager, or the Server Manager command-line tool, ServerManagerCmd.exe. You can start the Add Roles Wizard from either the Initial Configuration Tasks window or from Server Manager.
Hardware requirements for Windows Server Essentials and actual requirements will vary based on your system configuration and the applications and features you choose to install. Processor performance depends not only on the clock frequency of the processor, but also on the number of cores and the size of the processor cache. Storage space requirements for the system partition are approximate. Additional available storage space may be required if you are installing over a network.
Customizations options:
Add Post-Initial Configuration Customizations (PostIC.cmd) – Windows Server Essentials | Add Tasks and Links to Dashboard Home Page – Windows Server Essentials | Add Health Alerts – Windows Server Essentials | Configure Support for a Wireless Network – Windows Server Essentials | Customize Server Backup – Windows Server Essentials | Customize Shared Folders – Windows Server Essentials | Install Add-Ins – Windows Server Essentials | Add Branding – Windows Server Essentials | Add a Tab to Settings – Windows Server Essentials | Add Top-Level Categories to the Launchpad (Macintosh Operating System) | Change Media Streaming Settings – Windows Server Essentials | Change the Color of the Dashboard and Launchpad -Windows Server Essentials | Order and Group Dashboard Tabs – Windows Server Essentials | Add Third-Level Domain Names – Windows Server Essentials | Replace the List of Domain Name Providers – Windows Server Essentials | Customize Client Backup – Windows Server Essentials | Install Add-Ins During Setup – Windows Server Essentials | Add POR ID – Windows Server Essentials | Replace O365 Integration Module Endpoint URLs – Windows Server Essentials
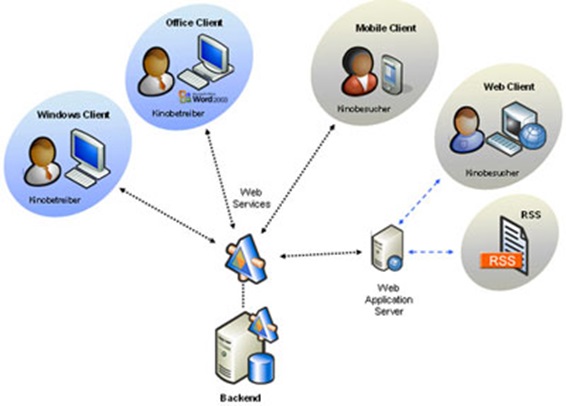
How to customize server or install new rules in our system based environment:
Roles Available for Installation in This Release
The following roles are available for installation by opening the Add Roles Wizard, either from the Initial Configuration Tasks window, or from Server Manager.
>Active Directory Certificate Services Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) provides customizable services for issuing and managing certificates in software security systems that use public key technologies. You can use AD CS to create one or more certification authorities (CA) to receive certificate requests, verify the information in the requests and the identity of the requester, issue certificates, revoke certificates, and publish certificate revocation data.
Applications supported by Active Directory Certificate Services include Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), secure wireless networks, virtual private networks (VPN), IP security (IPSec), Encrypting File System (EFS), smart card logon, Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS), and digital signatures.
>Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) stores information about users, computers, and other devices on the network. AD DS helps administrators securely manage this information and facilitates resource sharing and collaboration between users. AD DS is also required to be installed on the network in order to install directory-enabled applications such as Microsoft Exchange Server and for applying other Windows Server technologies such as Group Policy
>Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) provides Web single-sign-on (SSO) technologies to authenticate a user to multiple Web applications that use a single user account. AD FS accomplishes this by securely federating, or sharing, user identities and permissions, in the form of digital claims, between partner organizations.
>Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows servers to assign, or lease, IP addresses to computers and other devices that are enabled as DHCP clients. Deploying DHCP servers on the network automatically provides computers and other TCP/IP based network devices with valid IP addresses and the additional configuration parameters these devices need. /these are known as DHCP options,
>DNS Server
Domain Name System (DNS) provides a standard method for associating names with numeric Internet addresses. This lets users refer to network computers by using easy-to-remember names instead of a long series of numbers. Windows DNS services can be integrated with DHCP services, eliminating the need to add DNS records as computers are added to the network.